Our Products
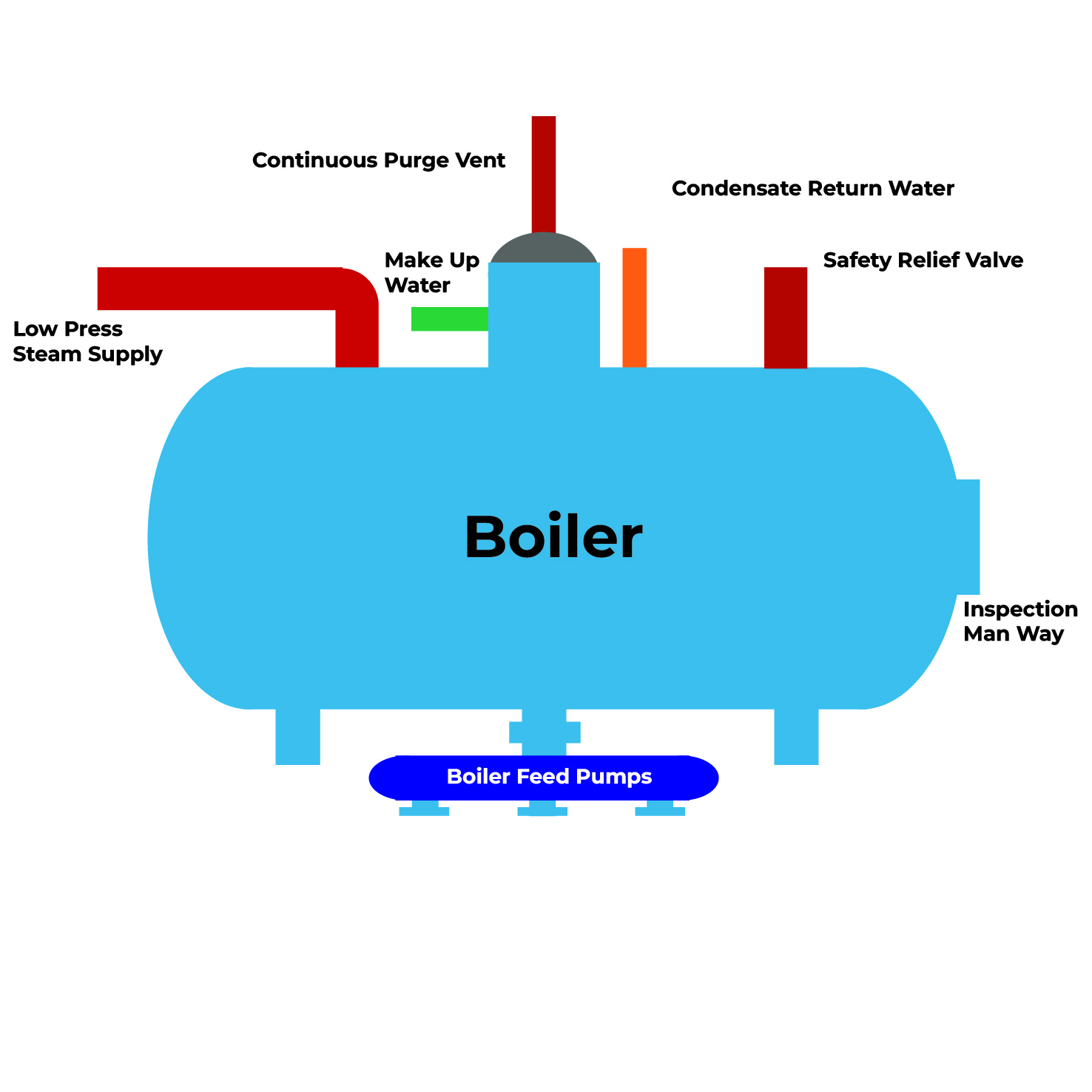
Boiler Treatment Technologies
Boiler treatment technology is essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of boiler systems.
Corrosion inhibitors play a crucial role by controlling oxygen corrosion, contributing to passivation, and ensuring that no inorganic solids are added to the feedwater, thereby improving overall boiler reliability.
Condensate treatment involves the use of polyamine and polyamine/neutralizing amine corrosion inhibitors to protect the condensate system from corrosion.
Internal treatment utilizes advanced boiler polymer patented treatments to reduce future deposition and potentially reduce existing deposit inventory and corrosion deposits.
By employing these technologies, boiler systems can operate more efficiently, with reduced maintenance needs and extended service life.

Cooling Water Technology
Cooling water treatment technology is designed to maintain system cleanliness, control microbial growth, and ensure efficient operation under various conditions.
Scale and corrosion inhibitor chemicals are crucial for keeping the system clean, utilizing the only halogen-stable technology available worldwide.
These inhibitors provide uncompromised performance under stressed conditions by employing stress-tolerant polymers (STP), alkaline-enhanced chemistry (AEC), and halogen-resistant azoles (HRA) in combination with phosphate-based steel corrosion inhibitors.
Micro bio control for cooling systems involves the use of both oxidizing and non-oxidizing biocides, along with biodispersants, to effectively manage microbial growth and prevent biofilm formation.
The auto control and monitoring system, enables online monitoring and ensures optimum chemical delivery, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and reliability of the cooling water system.
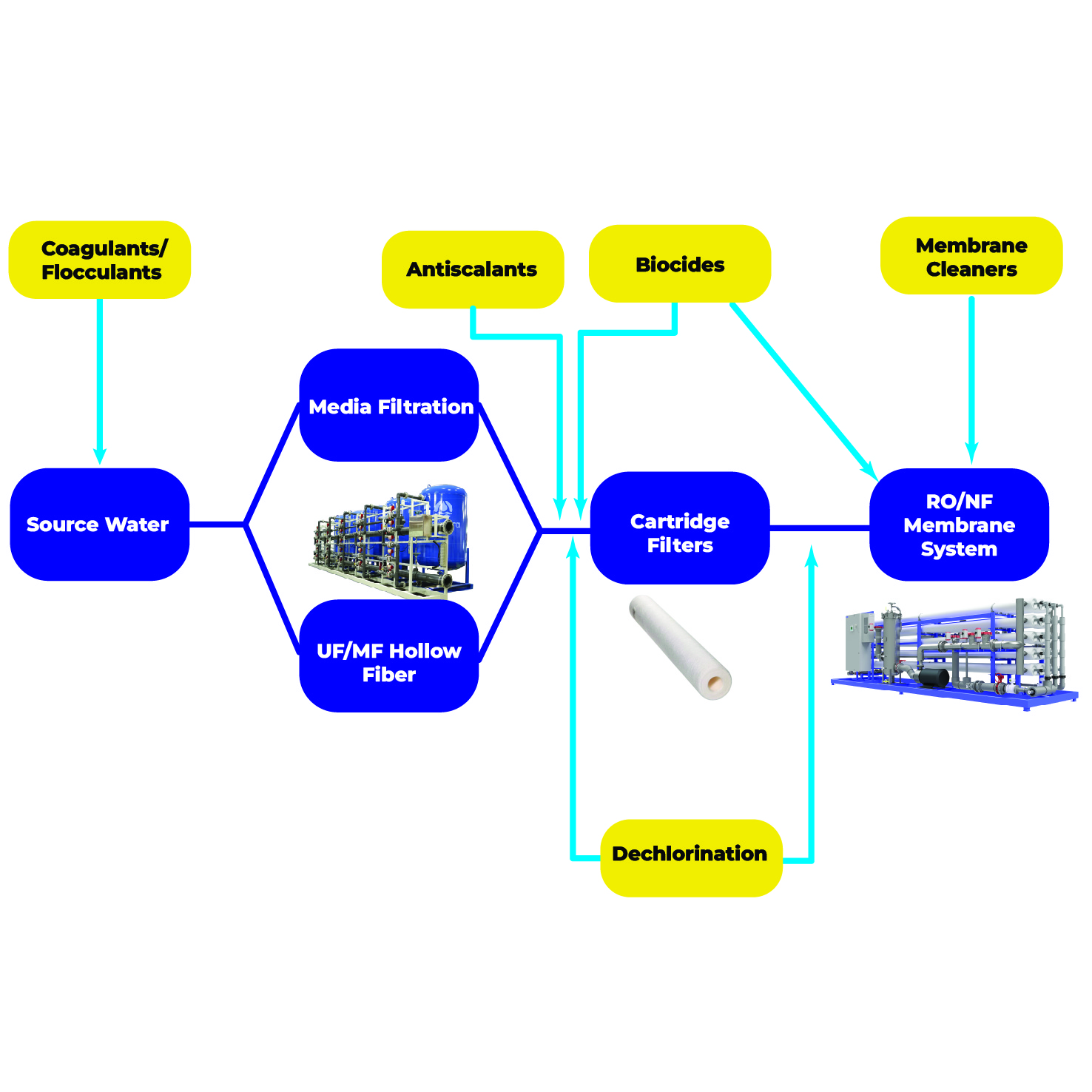
Membrane Chemicals Technology
Membrane chemical technology is essential for maintaining and optimizing the performance of membrane systems in water and wastewater treatment processes.
This technology involves the use of chlorine scavengers to protect membranes from chlorine damage, coagulants and flocculants to reduce the load on membranes during pre-treatment, and non-oxidizing biocides to control microbial growth on membrane surfaces.
Additionally, antiscalants are used to prevent scale formation, thereby reducing fouling and improving efficiency, while acid and alkaline cleaners are employed for regular cleaning to remove fouling and restore membrane performance.
By integrating these chemical agents, operators can enhance membrane protection, reduce fouling, prolong membrane life, and ensure consistent, high-quality water treatment.





































